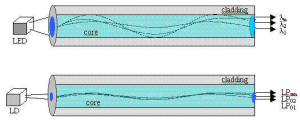
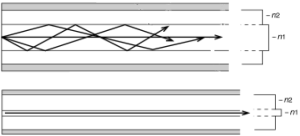
On the other hand,50μm optical fiber, has a minimum bandwidth requirement of 500/500 MHz/km. It is manufactured to have a peak bandwidth of ~980nm, thus providing good bandwidth at both wavelengths of interest. Because 50/125μm optical fiber has equal bandwidth at both short and long wavelengths, it is capable of supporting technologies bandwidth at both short and long wavelengths, it is capable of supporting technologies equally well at either window of operation.
The IEEE802.3z Gigabit Ethernet committee published two physical layer specifications for fiber, 1000BASE-SX (short wavelength) and 1000BASE-LX (long wavelength). VCSELs are used for 1000BASE-SX transceivers, so the SX electronics will be significantly less expensive than 1000BASE-LX transceivers using a conventional single-mode laser. IEEE 802.3z says that 1000BASE-SX and 1000BASE-LX will operate up to 550 meters on 500/500 MHz·km 50-micron fiber. However, according to IEEE, 1000BASE-SX will operate only up to 220 meters on standard 160/500 MHz·km or up to 275 meters with 200/500 MHz·km fiber. These operating distances are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: IEEE Distance Capability of Gigabit Ethernet over Fiber

While these distaces are far longer than those of 1000BASE-T and 1000BASE-TX on UTP cabling, in fact,the 62.5μm fibers do not reach 300m, the distance allowed for multimode fiber in the building riser by TIA-568, becomes problematic for new installations and for existing installations as well.
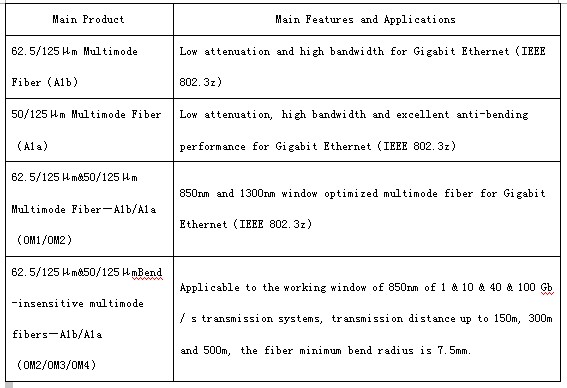
The distance limitations of 62.5/125μm may prevent an existing network from operating at gigabit per second speeds today, and may pose a greater concern in the event of any facility expansions in the future. 50-micron optical fiber, on contrast, can support over 95% of all the installed fiber network links, while still allowing distance expansions in the future. 50/125 optical fiber will support horizontal cabling (100 meters maximum), centralized cabling (300 meters maximum), and intra-building (inside) backbone cabling (300 meters maximum). The following products shows 62.5/125μm fiber, the products below is Duplex 62.5/125 OM1 Fiber.

This is a orange bulk 1000 foot spool of fiber optic cable which intended for large installations where you are completing the terminations. It is a 62.5μm multimode fiber designed to transmit data across shorter distances at LAN speeds. Multimode fiber is optimized to work with fiber optic equipment using light wave lengths of 850nm (nanometers) or 1300nm. The cord is duplex (two fibers) which means it permits synchronous communication between devices. The cladding diameter is 125 microns.
Short-wavelength laser-based technology, the most cost-effective fiber technology today,restricts the application of gigabit speeds on 62.5/125μm to the horizontal space and do not fully support the requirements of centralized and intra-building backbones. On the other hand, 50/125μm can be used for gigabit data rates in horizontal, centralized and intrabuilding backbone segments. The following products shows 50/125μm fiber, the products below is Duplex OM2 50/125 Multimode LC-SC Fiber.
It is specifically designed for use with today's narrower aperture components, this cable is fully compatible with multimode applications. The patented injection molding process provides each connection greater durability in resisting pulls, strains and impacts from cabling installs.
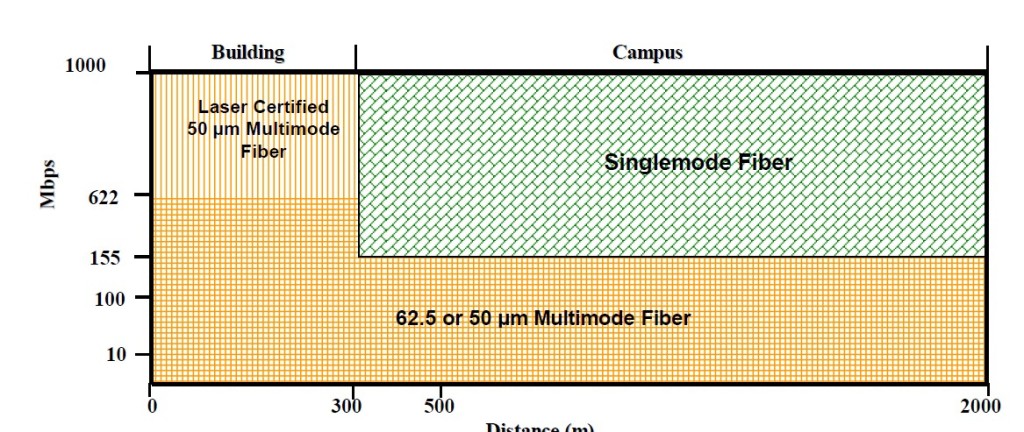
Additionally, 50/125μm infrastructure also works with the same LED-based LAN electronics that are installed and still being supplied. Today’s optical fiber hubs, switches, NIC cards and media converters are multi-mode products not specifically designed to operate with one fiber type or the other. The same connectors are utilized for 62.5/125μm and 50/125μm fiber networks. So, 50-micron optical fiber works well with today’s readily-available LED-based components while providing a seamless migration into laser-based technology, thus making it the best choice. Figure 1 shows the recommended application space for each fiber type.
Figure 1: Fiber Types, Data Rates and Distances